基于linux就改這么學的demo
簡單的Shell腳本Shell 是一個用 C 語言編寫的程序,它是用戶使用 Linux 的橋梁.Shell 腳本(shell script),是一種為 shell 編寫的腳本程序。業界所說的 shell 通常都是指 shell 腳本,,shell 和 shell script 是兩個不同的概念。Shell 腳本文件的名稱可以任意,但為了避免被誤以為是普通文件,建議將.sh 后綴加上,以表示是一個腳本文件。
例1:一個簡單的Shell腳步,顯示當前目錄
#!/bin/bash # 這個是一行注釋 pwd ls -al第一行:腳本聲明(#!)用來告訴系統使用哪種 Shell 解釋器來執行該腳本。第二行:第二行的注釋信息(#)是對腳本的注釋,不一定非要寫到第二行,根據需要來寫。第三行:第三行和以后的都是我們的腳本命令。
執行一下,執行shell腳本有兩種方法,設置執行權限或者bash 腳本名,這里用第二種,發現出現預期結果。
chmod +x ./test.sh #使腳本具有執行權限 ./test.sh #執行腳本 [root@virtualLinux file]# bash test.sh /home/vsftpd/java/file 總用量 8 drwxr-xr-x. 4 ftpuser ftp 65 10月 27 19:18 . drwx------. 3 ftpuser ftp 74 5月 13 00:15 .. drwxr-xr-x. 2 ftpuser ftp 63 10月 16 22:44 test drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 18 10月 7 19:32 test2 -rw-r--r--. 1 ftpuser ftp 46 10月 27 19:18 test.sh -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 230 10月 7 19:29 test.tar.gz [root@virtualLinux file]# 接收用戶參數在實際的使用過程中,腳本可能會根據情況傳遞參數,在Shell中,已經設置好了需要傳遞的參數方法。Linux 系統中的 Shell 腳本語言早就考慮到了這些,已經內設了用于接收參數的變量,變量之間可以使用空格間隔。例如$0對應的是當前 Shell 腳本程序的名稱,$#對應的是總共有幾個參數,$*對應的是所有位置的參數值,$?對應的是顯示上一次命令的執行返回值,而$1、$2、$3……則分別對應著第N個位置的參數值。

$* 和 $@ 的區別

例1:測試一下各個參數的用法
[root@virtualLinux file]# cat test1.sh #!/bin/bash echo "Shell腳本名為$0" echo "總共有$#個參數,分別是$*" echo "第一個參數為$1,第三個參數為$3" echo "執行ls -l 命令" ls -l echo "執行ls -l 命令,執行狀態碼為$?" [root@virtualLinux file]# sh test1.sh one two three Shell腳本名為test1.sh 總共有3個參數,分別是one two three 第一個參數為one,第三個參數為three 執行ls -l 命令 總用量 12 drwxr-xr-x. 2 ftpuser ftp 63 10月 16 22:44 test -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 211 10月 28 19:24 test1.sh drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 18 10月 7 19:32 test2 -rw-r--r--. 1 ftpuser ftp 46 10月 27 19:18 test.sh -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 230 10月 7 19:29 test.tar.gz 執行ls -l 命令,執行狀態碼為0 [root@virtualLinux file]# 判斷用戶的參數Shell 腳本中的條件測試語法可以判斷表達式是否成立,若條件成立則返回數字 0,否則便返回其他隨機數值。測試語句格式:
[ 條件表達式 ]按照測試對象來劃分,條件測試語句可以分為 4 種:? 文件測試語句;? 邏輯測試語句;? 整數值比較語句;? 字符串比較語句。
文件測試所用的參數
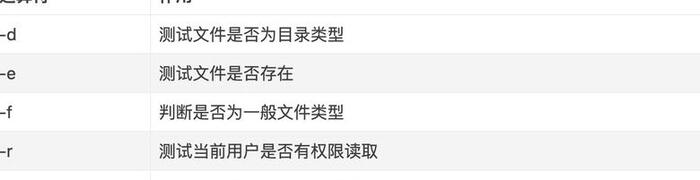
例1:判斷一個文件是目錄還是文件
[root@virtualLinux file]# [ -d /home/vsftpd/java/file ] [root@virtualLinux file]# echo $? 0 [root@virtualLinux file]#任何語言都離不開邏輯運算,在Shell腳本中也一樣,有與運算,符號&&、或運算,運算符||、非運算,運算符!。例1:與邏輯,判斷當前對象是目錄就輸出folder
[root@virtualLinux file]# [ -d test ] [root@virtualLinux file]# echo $? 0 [root@virtualLinux file]# [ -d test ] && echo "folder" folder [root@virtualLinux file]#例2:或邏輯,判斷當前用戶是否為root用戶
[root@virtualLinux file]# echo $USER root [root@virtualLinux file]# [ $USER = root ] || echo "login is root" [root@virtualLinux file]# su oracle [oracle@virtualLinux file]$ [ $USER = root ] || echo "login not root" login not root [oracle@virtualLinux file]$例3:非邏輯,判斷當前用戶是否為root用戶
[root@virtualLinux ~]# [ $USER = root ] && echo "root" root [root@virtualLinux ~]#由上面三個例子可以看出,在執行[ 條件表達式 ] 后,如果條表達式成了,&& 與條件后面的命令會執行,如果不成立,與條件后面的命令不會執行。如果條件表達式后面跟的是||或條件,如果條件表達不成立會執行,如果成立不會執行。
例4:演示條件表達式的執行
[root@virtualLinux ~]# [ ! $USER = root ] && echo "root" || echo "other" other [root@virtualLinux ~]#例4可以看出,先條件判斷用戶為root,然后!取非,反條件,執行個與運算不成立,執行的第二或運算,輸出的other。
在linux中和java正好相反,字符串比較用等號,對數字的操作不能使用數學中的比較符號。
整數比較的運算符
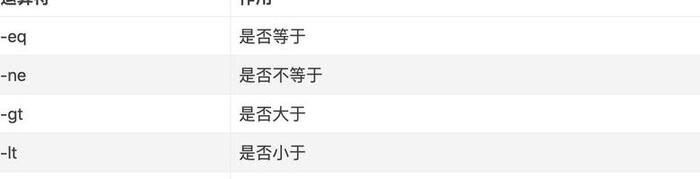
例1:做一個簡單的數字大小判斷
root@virtualLinux ~]# [ 10 -eq 10 ] [root@virtualLinux ~]# echo $? 0 [root@virtualLinux ~]# [ 10 -lt 2 ] [root@virtualLinux ~]# echo $? 1 [root@virtualLinux ~]# [ 10 -gt 2 ] [root@virtualLinux ~]# echo $? 0 [root@virtualLinux ~]#常見的字符串比較

例1:一個沒有定義的變量判斷為空后賦值再次空判斷
[root@virtualLinux ~]# echo $String [root@virtualLinux ~]# [ -z $String ] [root@virtualLinux ~]# echo $? 0 [root@virtualLinux ~]# String="123" [root@virtualLinux ~]# echo $String 123 [root@virtualLinux ~]# [ -z $String ] [root@virtualLinux ~]# echo $? 1 [root@virtualLinux ~]# 流程控制語句if、for、while、case 在Shell腳本中必不可少的,應該說在現在所有的編程語言都離不開這4中流程控制語句。
if 條件語句if 條件語句分為單分支結構,雙分支結構,多分支結構三種。
單分支結構單分支結構就是只有一個條件,如果條件成立,執行預設的命令。語法格式
if 條件 then 命令 fi例1
[root@virtualLinux shell]# ls test1.sh test.sh [root@virtualLinux shell]# vim test2.sh [root@virtualLinux shell]# cat test2.sh #!/bin/bash File="test.sh" if [ -e $File ] then echo "find file" fi [root@virtualLinux shell]# bash test2.sh find file [root@virtualLinux shell]# 雙分支結構雙分支結構語法關鍵字if then else if 它只進行一次if條件,如果滿足執行then 不滿足執行else。ping 命令中 -c定義重試次數,-i定義重發間隔時間,-W定義參數超時等待時間例1:ping 百度,如果能連通輸出在線,不能連通輸出不在線
[root@virtualLinux shell]# more test3.sh #!/bin/bash ping -c 3 -i 0.5 -W 3 www.baidu.com if [ $? -eq 0 ] then echo "on-line" else echo "off-line" fi [root@virtualLinux shell]# bash test3.sh PING www.a.shifen.com (180.97.33.108) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from www.baidu.com (180.97.33.108): icmp_seq=1 ttl=54 time=40.7 ms 64 bytes from www.baidu.com (180.97.33.108): icmp_seq=2 ttl=54 time=39.5 ms 64 bytes from www.baidu.com (180.97.33.108): icmp_seq=3 ttl=54 time=37.5 ms --- www.a.shifen.com ping statistics --- 3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 1004ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 37.519/39.277/40.771/1.340 ms on-line [root@virtualLinux shell]# 多分支結構多分支結構就是if,then,elsif,else,fi關鍵字組成,相當于口語的如果。。。。那么,如果。。。那么。。。在 Linux 系統中,read 是用來讀取用戶輸入信息的命令, 能夠把接收到的用戶輸入信息賦值給后面的指定變量,-p 參數用于向用戶顯示一定的提示信息。例1:根據輸入的成績輸出對應的字符串
[root@virtualLinux shell]# vim test4.sh [root@virtualLinux shell]# more test4.sh #!/bin/bash read -p "請輸入成績:" GRADE if [ $GRADE -ge 80 ] then echo "優" elif [ $GRADE -lt 80 ] && [ $GRADE -ge 70 ] then echo "良" elif [ $GRADE -lt 70 ] && [ $GRADE -ge 60 ] then echo "合格" else echo "不合格" fi [root@virtualLinux shell]# bash test4.sh 請輸入成績:85 優 [root@virtualLinux shell]# bash test4.sh 請輸入成績:55 不合格 [root@virtualLinux shell]# bash test4.sh 請輸入成績:76 良 [root@virtualLinux shell]# Linux shell]# for 條件循環語句for 循環在處理范圍數據時,是最適合是,它可以讀取文本數,也可以做自己的循環語法格式
for 變量名 in 取值列表 do 命令序列 done for 變量名 in 列表文件 do 命令序列 done例1:循環輸出數字或者目錄
[root@virtualLinux shell]# ls test1.sh test2.sh test3.sh test4.sh test5.sh test.sh [root@virtualLinux shell]# cat test5.sh #!/bin/bash for num in {1..10} do echo $num; done for ((i=1;i<10;i++)); do echo $i; done echo ‘在for執行命令循環,需用反引號``’ for str in `ls`; do echo $str; done [root@virtualLinux shell]# bash test5.sh 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 ‘在for執行命令循環,需用反引號’ test1.sh test2.sh test3.sh test4.sh test5.sh test.sh [root@virtualLinux shell]#最后一個執行ls 命令的也可以執行文件,例如cat xxx.txt
while 條件循環語句while是不斷的重復循環執行,直到循環條件為false,或者執行exit 0命令才會退出循環語法格式
while 條件 do 命名序列 done列1:做一個循環
[root@virtualLinux shell]# cat test6.sh #!/bib/bash flag=true num=1 while $flag do echo $num; num=`expr $num + 1`; if [ $num -eq 3 ] then flag=false; fi done num2=5 while true do echo $num2 num2=`expr $num2 + 1`; if [ $num2 -eq 7 ] then exit 0 fi done [root@virtualLinux shell]# bash test6.sh 1 2 5 6 [root@virtualLinux shell]# case 條件語句case條件就是java中的switch非常相似,使用場景基本相同
case 變量值 in 條件1) 命令1 ;; 條件2) 命令2 ;; 條件3) 命令3 ;; ...... *) 默認命令 esac1、) 相當于其他語言中的default。2、除了)模式,各個分支中;;是必須的,;;相當于其他語言中的break3、 | 分割多個模式,相當于or
例1:一個簡單的case 語句
[root@virtualLinux shell]# cat test8.sh #!/bin/bash read -p "請輸入一個字符,并按 Enter 鍵確認:" KEY case "$KEY" in [a-z]|[A-Z]) echo "您輸入的是 字母。" ;; [0-9]) echo "您輸入的是 數字。" ;; *) echo "您輸入的是 空格、功能鍵或其他控制字符。" esac [root@virtualLinux shell]# bash test8.sh 請輸入一個字符,并按 Enter 鍵確認:1 您輸入的是 數字。 [root@virtualLinux shell]#logo設計網(www.just4love.cn),專業的logo免費設計在線生成網站,全自動智能化logo設計,商標設計,logo在線生成!
歡迎使用logo設計網制作屬于您公司自己的logo,不僅專業而且經濟實惠,全方位滿足您公司品牌化、視覺化的需求。







 [掃碼關注我們]
[掃碼關注我們]
